Facial Feminization

What is facial feminization?
Facial feminization is a surgery that treats many aspects of the face to make your face appear to be more feminine, but most importantly still look like you. Not every person would benefit from or desire all aspects of facial feminization. This is a very personal decision and there is no “cookie cutter” surgical plan as every person is different.
We like to think of the face in three regions
· Upper third including the eyebrows, orbits, forehead and the hairline
· Middle third including the eyes, cheeks and the nose
· The lower third including lips, jaw, chin, neck and tracheal cartilage
Each patient’s surgery and results are different.
What to consider
Before your first consultation, we encourage you to:
· Consider your goals and priorities of surgery. Whether your goals are to reduce misgendering, improve your personal self image or a mix of both.
· Think about areas of your face that you like it will be important for us to not change those aspects of your face. Everyone has feminine and masculine traits to their face, and we will ask you to consider on yourself which traits fit your personal image and which ones that are particularly bothersome.
· Consider aspects of your face that might be from your family. For example your “grandmonther’s nose” as you may desire to leave these areas unchanged.
· Write down your questions and bring them with you to your visit.
· Ask a support person to come with you. Ideally, this is the same person who will care for you after surgery.
Your first consultation
Your first consultation is an opportunity for us to learn about your hopes and goals. You will be given a questionnaire to help us meet your needs and measure the results. Your surgeon will review various surgical options and explain the process.
Once we understand your goals, we will:
· Evaluate your anatomy. This involves taking measurements of your face and documenting any asymmetries as they are seen in all faces.
· Assess your overall health to see which surgeries can meet your goals. You may be asked to lose weight or make lifestyle changes to prepare your body for surgery.
· Ask you to have a CT scan completed of your face This is needed to get a better idea of bony anatomy and helps with surgical planning
A fair amount of time is spent during the consultation with your surgeon, but you may also meet the other members of your care team.
Surgical Options
Upper Third
This area addresses the hairline, the forehead and the orbits (bony structure around the eyes).
Forehead shortening or hairline advancement
Goals: This surgery is used to reduce the distance of the eye brows to the forehead and help improve a masculine shaped hairline. Though hairline shape and forehead height are different from person based on ethnic background and age typically a more feminine hairline will be U shaped and will be shorter in height.
Ideal candidate: Person with mild to moderate hair loss in the temple area that would benefit from a few centimeters of advancement. Those with significant loss may consider use of hair piece or wig to improve hairline when there is significant hair loss.
Surgical approach: Incision is made at the front edge of the hairline on the forehead in the hair bearing scalp above the ears. Small area of scalp is shaved around these areas in order to access the scalp. The skin is raised over nearly all of the scalp and the hair bearing scalp is moved foreword and part of the forehead is excised.
Limitations: Stiffness of the scalp is different from person to person. Some scalps can be shortened more than others. Typically 1-2cm of advancement is possible in most patients more can be achieved in few. Those with significant hair loss are not candidates. Those even after forehead shortening may benefit from additional hair transplant in the lateral temples to augment the forehead shortening results and to improve the hairline further.
Hair Transplant (Not offered )
Goals: To add hair to areas of recession and give a more rounded hairline to the scalp
Ideal candidate: Someone with minimal hair recession that would need just a small bit of hair for shaping. Some may choose to do hair grafting after forehead shortening to enhance their surgical results.
Limitations: Often not covered by insurance. People with significant hair loss are not candidates.
Frontal Bossing or Forehead Ridge:
Goals: To reduce the projection of the frontal bossing or ridge between the eyebrows. This area grows during puberty when frontal sinus forms and is more pronounced in a masculine face. Goals are to make a soften rounded forehead with a gently slope.
Ideal candidate: An improvement can be made in nearly all patients results will differ from patient to patient based on their anatomy.
Surgical approach: Access is needed from the scalp. Ideally this case is done at the same time as the forehead shortening as the forehead shortening incisions expose also the forehead. If no forehead shortening is needed the incision is made a few centimeters behind the forehead. A small stripe of hair will be shaved next to the incision to allow access to the scalp. The forehead is then exposed using a power burr the forehead will be reshaped. In many it will be necessary to use a saw to remove part of the bone on the frontal sinus which will be reshaped and then replaced with screws and plates.
Limitations: We are limited by the bony anatomy of the forehead. Some patient will have differently thickened bones and differently shaped frontal sinuses or will not have frontal sinuses at all. This will change what can be accomplished during surgery though an improvement is expected in all patients.
Orbit remodeling
Goals: To reshape the lateral upper orbits to “Open the eyes” to give a more feminine shape and make the eyes appear larger. This is completed by shaving down the lateral upper portion of the orbit bone around the eye.
Ideal candidate: Someone that is also having frontal bone remodeling or set back with or without forehead shortening or hairline advancement
Surgical approach: Though the same incision as with the forehead shortening
Limitations: Amount of bone that can be removed is different from patient to patient and results will therefore be different from patient to patient.
Brow lift
Goals: To raise the eye brow to the position at or slightly above the level of the upper orbital bone. This again opens the eyes and give a more feminine look to the upper third of the face
Ideal candidate: Someone that is also having frontal bone remodeling or set back with or without forehead shortening or hairline advancement
Surgical approach: Though the same incision as with the forehead shortening. Long lasting sutures will be used to anchor the skin to the skull to position the eye brows in a higher position.
Limitations: Patient will have their own asymmetries that can be improved but no always corrected with this procedure. Skin quality and bony anatomy will dictate how much of a brow lift can be achieved.
Middle Third
This areas includes the eyes, nose and cheeks
Upper and lower Blepharoplasty
Goals: to remove excess skin and reduce or redistribute fat around the orbit. Similar and in conjunction with a brow lift a blepharoplasty can open the eye to give a more feminine appearance to the eye. This is also a common procedure in facial aging to give a more awake and youthful look to the eyes.
Ideal candidate: Someone with excess skin on the upper or lower eye lid. Someone with lower eye lid “Bags”.
Surgical approach: Upper blepharoplasty is completed with an incisions along the crease of the upper eyelid. The lower blepharoplasty is completed though an incisions inside of the eye or an incision just below the lower lash line
Limitations: May be considered to be a cosmetic procedure in some patients. Those with dry eyes or recent eye surgery may not be candidates for surgery. This portion may not be covered by insurance.
Rhinoplasty
Goals: To bring balance to the face as a whole by refining aspects of the nose. Needs in rhinoplasty will be different in every patient. Rhinoplasty can change the width, length, and projection of the nose as well as changing the shape of the nose including the dorsum, tip and nostrils.
Ideal candidate: Those with large or wide nose with a boxy tip and/or a dorsal hump looking for refinement in their nose.
Surgical approach: Operation is completed through a small incision between the nostrils and into the lining of the nose. Sometime 2 very small incision is made on the outer side of the nose in-between the eyes. After surgery the nose is dressed with an outside splint and possibly an inside splint as well. Edema from rhinoplasty can last months to even a year. Bruising especially around the eyes is to be expected.
Limitations: Those with thick nasal skin will limit the amount of refinement that can be seen especially in the tip. Small changes can be expected but drastic large changes may not always be attainable in those with thick skin.
Fat grafting for facial augmentation
Goals: To bring more fullness to the apples of the cheeks to give a more rounded or heart shaped appearance to the face. Fat can also be injected in the temple area to bring balance to the face in some patient. Lip augmentation to add balance and fullness to the lips can also be accomplished.
Ideal candidate: A patient with fat loss or a reduced fat in the cheek, temple, or lips that would benefit from augmentation
Surgical approach: Fat is taken with small cannulas from usually the abdomen but other areas can be used as well. The fat once processes is then injected into the cheeks to add volume.
Limitations: Fat take can be variable therefore multiple fat grafting session may be needed to get desired results. Results can also change with changes in weight.
Face Lift/Neck lift
Goals: To remove loose skin of the face and tighten underlying structure of the face to give a more youthful look to the face.
Ideal candidate: Patient with excess skin with wrinkling of the skin with loss of deep facial support in the face and neck who is a non smoker
Surgical approach: Incision is made in front and behind the ear and skin flaps are raised to the cheek and into the neck. Sometimes an additional incision is made under the chin to allow better access to the neck during a neck lift.
Limitations: Usually a cosmetic procedure not covered by insurance. This procedure is only offered to non smokers
Lower Third
This area covers the lips jaw and chin
Lip Lift
Goals: To decrease the length of the upper lip to give slightly more tooth show with smile and to slightly upturn the lip to give the appearance of a fuller upper lip.
Ideal candidate: Patient with elongated upper lip who does not have significant tooth show in repose or with smile.
Surgical approach: incision is made under the nose to remove tissue from the lip and closed in a thin line hidden under the nose.
Limitations: Lip will continue to lengthen with age as it does in all people.
Genioplasty
Goals: To reposition the chin to give a more feminine look to face this can involve making the chin shorter and/or less wide with a more v shape and may also involve moving the chin forward or back to add harmony to the face.
Ideal candidate: Patient with a widened or elongated chin
Surgical approach: incision is made along the gums on the lower lip. A saw or a burr are used to reshape the chin. Plates, screw or wires may be used to secure the bone.
Limitations: Those with thicker skin will have less of a dramatic change than those with thinner skin and swelling may take longer to resolve.
Mandible remodeling
Goals: To change the shape of the jaw to give a more v shaped face and reduce the width of the jaw bone
Ideal candidate: Someone with wide winged mandible
Surgical approach: Incision are made inside of the cheek
Limitations: Those that have fuller faces or extra soft tissue of the face may not appreciate changes made to the mandible.
Thyroid cartilage shaving
Goals: To reduce the appearance of the thyroid cartilage known also as the “Adam’s apple”. This makes a flatter neck appearance from the side.
Ideal candidate: Patient with a large amount of visible thyroid cartilage.
Surgical approach: An incision is made on the front portion of the neck. The cartilage is then partially removed and covered in a layered closure
Limitations: Vocal cords connect to the thyroid cartilage and may limit the amount that can be removed. Though in most cases a vast improvement can be achieved in some a residual amount of cartilage may remain.
After Care
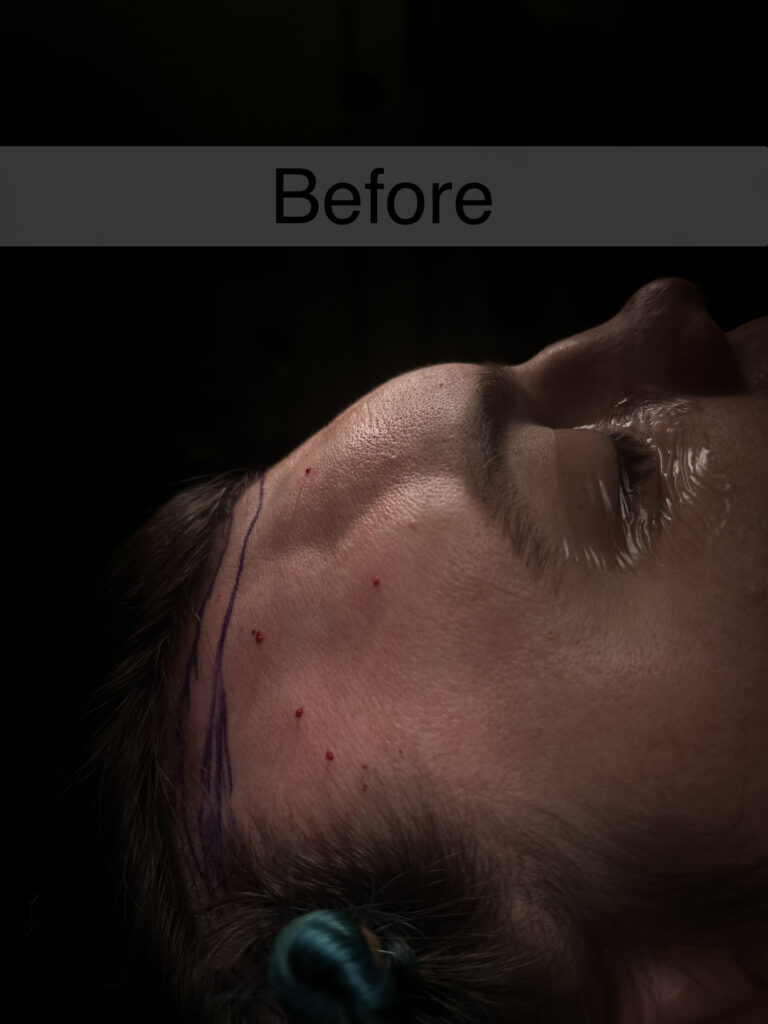
Healing from FFS
Healing from FFS with depend on what surgeries are done and can be variable from person to person. It is not uncommon for patients to have some anxiety after surgery or a feeling a claustrophobia among patients with large facial surgeries.
Swelling and bruising can be significant after surgery this is expected. We encourage sleeping with the head of the bed elevated to help decrease swelling. Avoid exertion, straining, bending or lifting for 2 weeks after surgery. We will discuss activity restrictions and limitations at your post op visits. We encourage walking short distances for the first few post-operative days and then progress as tolerated. Elevate your head by sleeping in a recliner or propped up in bed on several pillows for the first 3-5 days after surgery to help minimize bruising, swelling, and discomfort. A room humidifier/vaporizer will assist to keep nasal secretions more liquefied to aid in draining of nasal passages. Do not wear glasses for 6 weeks after surgery. No contact sports for 2 months post-op